A Strong Nucleophile Will Favor Which of the Following
Since salts are insoluble in non-polar solvent therefore non-polar. Weak nucleophiles favor the _____ reaction mechanism.
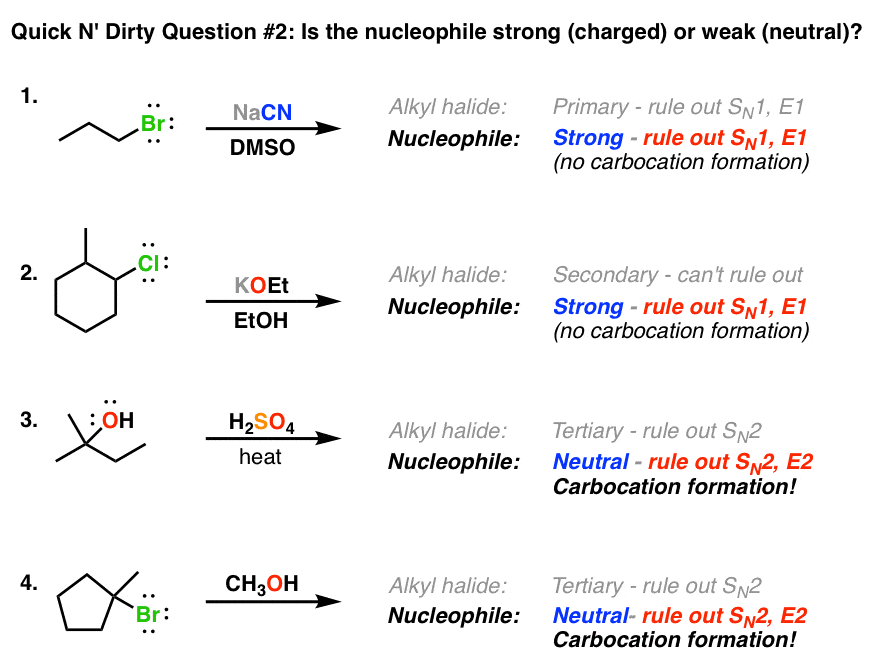
Deciding Sn1 Sn2 E1 E2 2 The Nucleophile Base
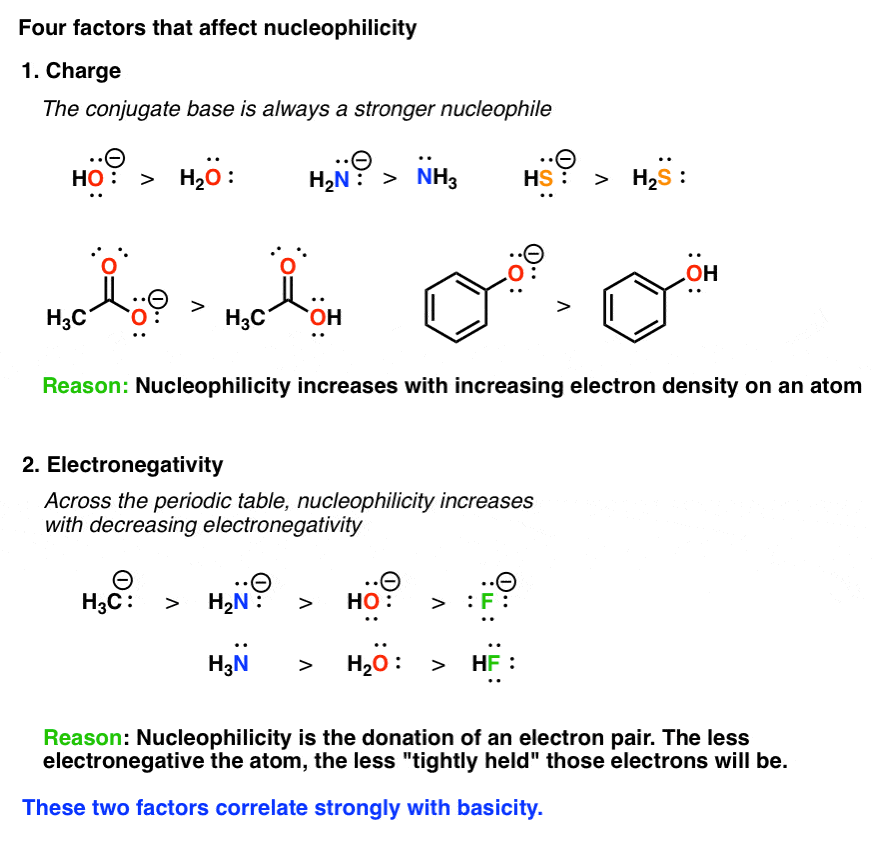
The stronger base equals the stronger nucleophile negatively charged nucleophiles are stronger than its conjugate acid and right to left across a row nucleophilicity increases as.
. Start studying OC strong nucleophiles bases E1 E2 Sn1 Sn2. O CH2OH O OH. Strong nucleophiles are required in S N 2 reactions and strong nucleophile are usually negatively charged species such as OH CH 3 O CN etc.
If weak SN1 or E1. These anions must stay with cations in salt format like NaOH CH 3 ONa etc. Bigger So I-is a better nucleophile than F-.
If it is a non-bulky base look further into the substrate primary substrates do SN2 secondary and tertiary do E2 as the major mechanism. The nature of the halogen substituent on the alkyl halide is usually not very significant if it is Cl Br or I. Both nitrogen and sulphur have lone pairs but sulphur is less electronegative than nitrogen hence sluphur lone pairs are more available for more donation.
View chapter Shortcuts Tips. Important Diagrams Problem solving tips. What Makes a Good Nucleophile.
Weaker nucleophiles such as water or alcohols favor the S N 1 mechanism. While in case of C 2. Strong nucleophiles favour S_N2 mechanism.
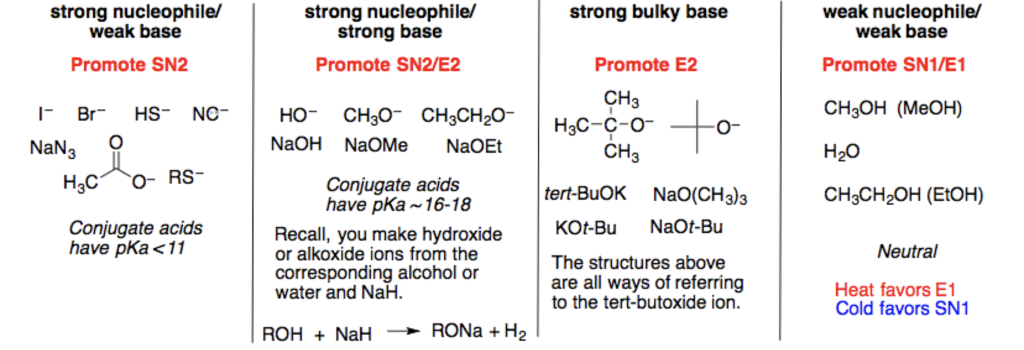
Alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions with nucleophiles. 3 The solvent. Strong Nucleophiles Usually anions with a full negative charge easily recognizable by the presence of sodium lithium or potassium counterions Participate in SN2-type substitutions Examples.
Strong nucleophiles favor the SN2 mechanism over the SN1 mechanism. Reaction with a weak nucleophile will favor the _____ mechanism for nucleophilic substitution whereas reaction with a strong nucleophile in high concentration will favor the _____ mechanism SN1 SN2 Select all the statements that correctly describe the mechanism of the SN1 reaction. Start studying Common StrongWeak Nucleophiles.
Wants to give away electrons good Lewis base. An SN1 mechanism forms a _____ as a reactive intermediate and the mechanism has _____. Strongest nucleophile among the following is.
Powerful nucleophiles especially those with negative charges favor the S N 2 mechanism. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Lets look at how we can tell the difference between a strong and weak nucleophile.
2 If it is a strong bulky base E2 only. Polar Aprotic Solvents Favor S N 2 Reactions. HO- better than H2O bases always better than their conjugate acids better than less electronegative atom means more willing to give up e- HS-better than Cl-NH3 H2O What Makes a Good Nucleophile.
A primary substrate with a strong nucleophile follows the S N 2 path but when there is a strong hindered base the reaction favors the E2 reaction. Which of the following is a strong nucleophile. When a substrate is secondary and reacts with an unhindered weaker base it follows the S N 2 reaction and when it reacts with an hindered stronger base it follows the E2 reaction.
S_N1 proceed with polar protic solvents like water carboxylic acids and alcohols. S_N2 mechanisms are favored when a strong nucleophilebase is involved. Therefore Option B is incorrect.
Strong nucleophiles favor the ___ mechanism over the ___ mechanism. O LOH Н N IV o none of these IV. Equilibrium favors the products of nucleophilic substitution when the leaving group is a _____ base than the nucleophile.
Next S_N2 mechanisms favor a polar aprotic solvent such as DMSO. The polar solvent increases the carbocation stability and they both favor S_N1 mechanism. SH is strongest nucleophile.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. For the following example show the mechanism and predict the products including stereochemistry. O All of these O H2O O NHA Which of the following.
Polar aprotic solvents have strong dipole moments to enhance solubility and have no protic protons as in alcohols or amines for example which will form hydrogen bonds with anions. NaOCH3 any NaOR LiCH3 any RLi NaOH or KOH NaCN or KCN NaCCR acetylide anion NaNH2 NaNHR NaNR2 NaI LiBr KI NaN3. 1 Determine if the baseNu is strong or weak.
Chemistry questions and answers. Protic solvents favor SN1 mechanism and aprotic solvents favor the SN2. If strong SN2 or E2.
Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques. Which of the following is a strong nucleophile. O All of these O H2O O NHA Which of the following solvent is best for SN1.
View solution Among the following the strongest nucleophile is. An SN1 mechanism forms a carbocation as a reactive intermediate and the mechanism has two steps first order. Negative charge is involved in conjugation so less available for donation.
O CH2OH O OH. S_N1 proceeds with strong nucleophiles that have low concentration. Strong nucleophiles favor substitution and strong bases especially strong hindered bases such as tert-butoxide favor elimination.
View solution View more. Polar aprotic solvents favor the S N 2 mechanism by.
What Makes A Good Nucleophile Master Organic Chemistry

Solved Strong Nucleophile Weak Base Strong Nucleophile Chegg Com
No comments for "A Strong Nucleophile Will Favor Which of the Following"
Post a Comment